By Danny Munch – American Farm Bureau Federation Economist
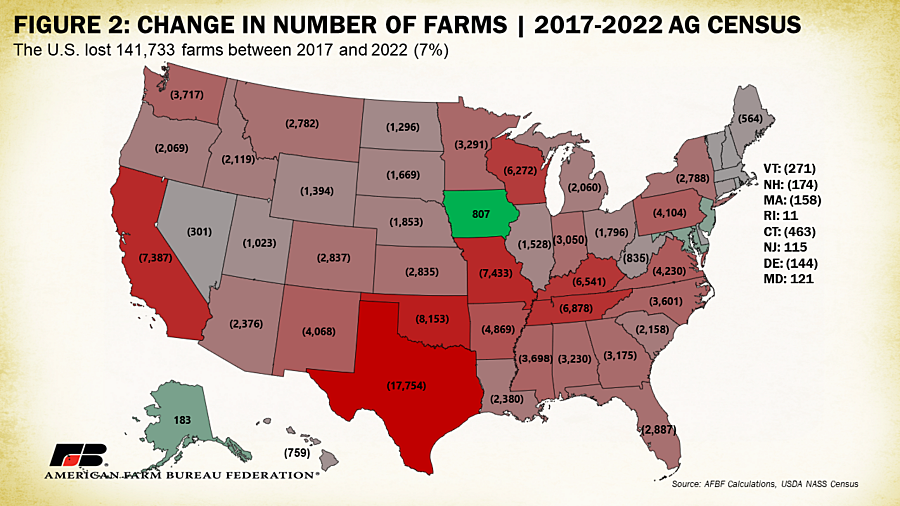
Between 2017 and 2022, the number of farms in the U.S. declined by 141,733 or 7%, according to USDA’s 2022 Census of Agriculture, released on Feb. 13. Acres operated by farm operations during the same timeframe declined by 20.1 million (2.2%), a loss equivalent to an area about the size of Maine. Only 1.88% of acres operated and 1% of farm operations were classified under a non-family corporate farm structure.
Conducted every five years, the Census of Agriculture collects data on land use and ownership, producer characteristics, production practices, income and expenditures. USDA defines a farm as an operation that produced and sold, or normally would have sold, $1,000 or more of agricultural products during the census year.
While the number of farm operations and acres operated declined, the value of agricultural production increased, rising from $389 billion in 2017 to $533 billion in 2022 (40% nominally and 17% adjusted for inflation). These updated numbers highlight the continuing trend of fewer operations farming fewer acres of land but producing more each year.
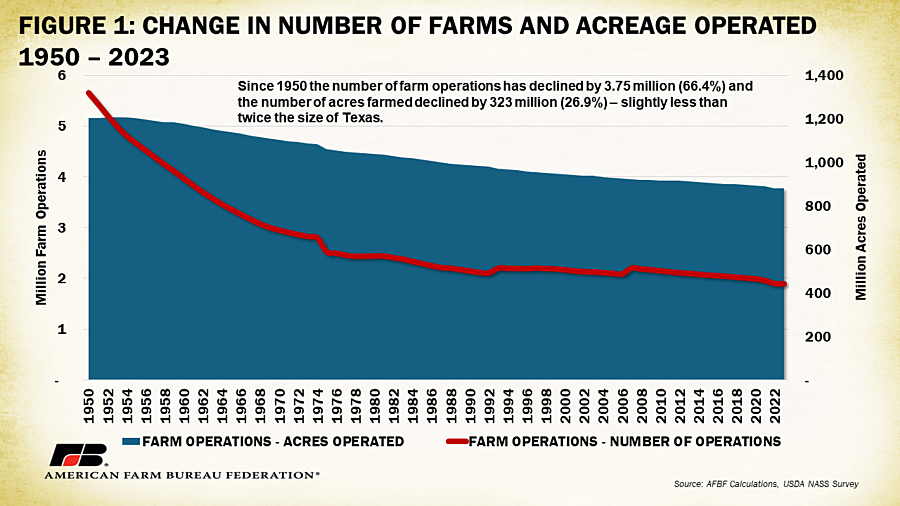
In addition to Ag Census data, USDA releases survey-based estimates on farm numbers once every year. Using this annual survey data dating back to 1950, the trend of fewer operations farming fewer acres becomes even more obvious. Since 1950, the number of farm operations has declined by 3.75 million (66%) and the number of acres farmed declined by 323 million (27%) – slightly less than twice the size of Texas. Technological advancements that have increased productivity, such as feed conversion ratios in livestock and yield per acre in crops, have allowed farmers and ranchers to produce more with less even as the U.S. population more than doubled, going from 159 million in 1950 to 340 million in 2023, and the global population more than tripled (2.5 billion to 8 billion) during the same period.
Farm Operations
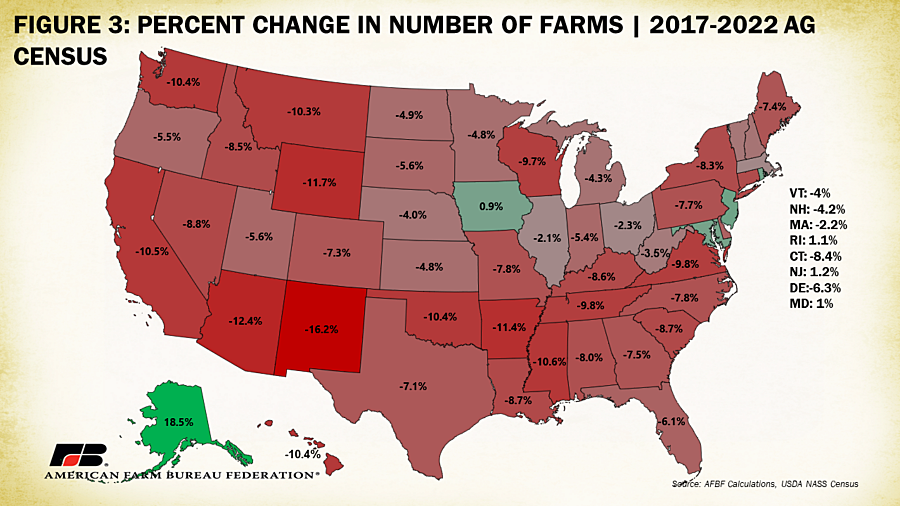
Between 2017 and 2022 all states but five (Alaska, Iowa, Maryland, New Jersey and Rhode Island) lost farms. Texas had the largest numerical loss – nearly 18,000 farm operations – followed by Oklahoma (-8,153) and Missouri (-7,433). Iowa gained the most farm operations (+807) followed distantly by Alaska (+183). In terms of percentage loss of farm operations, New Mexico experienced the largest decline (-16.2%) followed by Arizona (-12.5%) and Wyoming (-11.7%). Alaska’s 183-farm gain was the largest percent increase at 18.5%. Though the presence of regional trends in farm operation losses appears limited, drought conditions that battered much of the West in 2021 and 2022 may be responsible, in part, for higher farm loss percentages in those states. Across states that gained farms, most were within the category of earning over $1 million in sales except in Alaska where the biggest gains were in farms earning between $5,000 and $50,000.
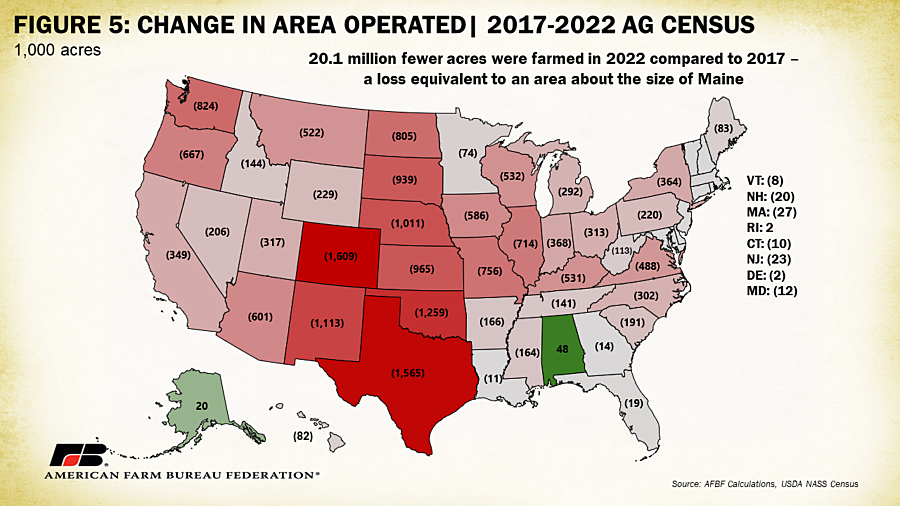
Area Operated
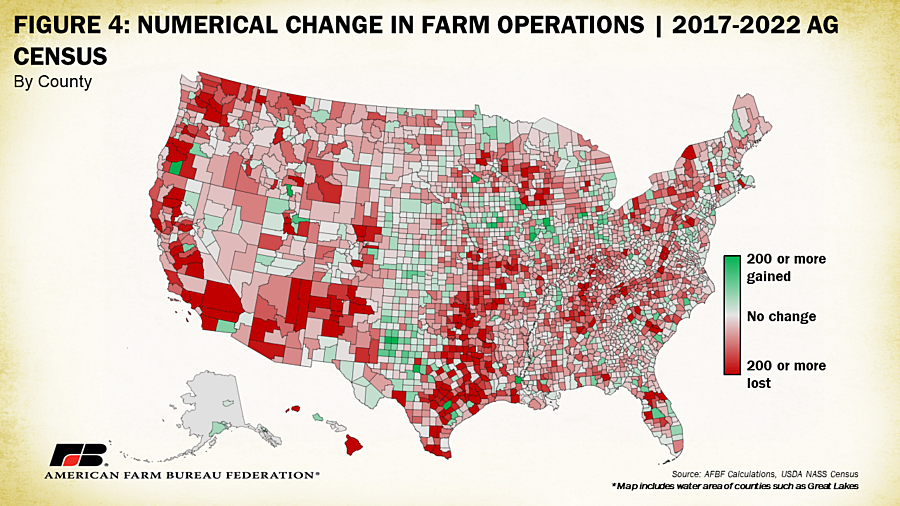
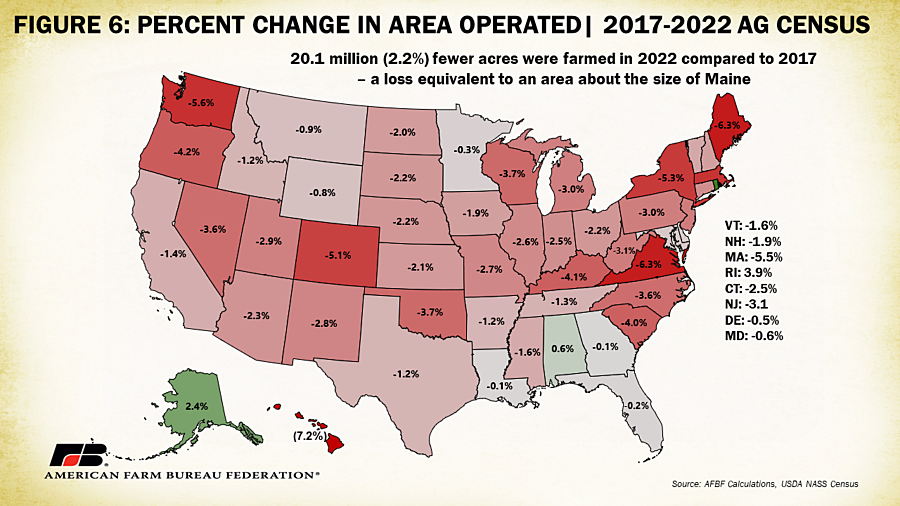
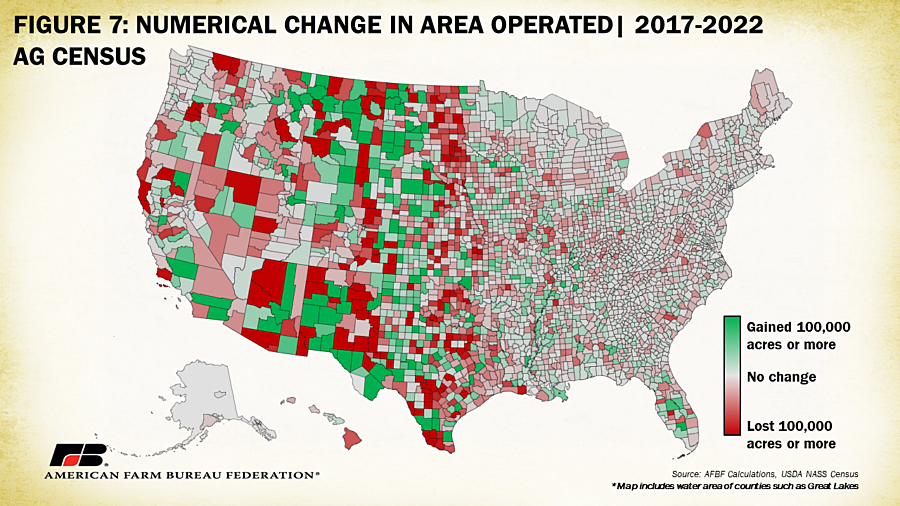
The 2022 census also indicates a decline of just over 20 million acres (2.2% of total) in acreage operated. Colorado led in terms of numerical decline, with 1.6 million fewer acres being farmed in 2022 compared to 2017, followed by Texas (-1.56 million), and Oklahoma (-1.26 million). Only three states, Alabama, Alaska and Rhode Island, had increases in operated area. By percent decline, the map of operated acreage looks quite different. Hawaii leads with a loss of 7.2% of operated area followed by Virginia and Maine both experiencing a loss of 6.3% and Washington experiencing a loss of 5.6% between 2017 and 2022. Counties in the West had the largest swings in acreage operated, likely linked to the sheer size of counties with a significant proportion of open and undeveloped land.
Even minor declines in farmed area can have a significant impact on the rural identity of states with smaller acreage and higher rates of commercial and residential development. The more land shifted out of agriculture production, the harder it is to return those acres to farming. Diminished production capacity within specific states and regions heightens dependence on purchases from other states or countries. For instance, Hawaii faces a unique situation with only enough production and food storage capacity to sustain itself for seven days, exacerbated by a 7% loss in actively farmed land over the past five years. In New England, on a weight basis, farmers produce only about 21% as much food as the states consume (with a portion of that going to outside buyers). Researchers have estimated that in order to reach 30% self-food-sufficiency, the six New England states would have to maximize the use of 401,000 existing underutilized acres and clear an additional 588,000 acres of land. Instead, acres operated in New England dropped by 145,000 between 2017 and 2022. Local regulatory dynamics, land use pressures and costs, and variations in cultural interests contribute to the shifting landscape of farming, often pushing it farther away from population centers.
###
American Farm Bureau Federation


